Pros
Made from renewable and sustainable plant materials rather than finite petroleum oil.
The carbon footprint of manufacturing bioplastics is reportedly 75% lower than PET and PS.
Some bioplastics are biodegradable and compostable. They can improve soil fertility.
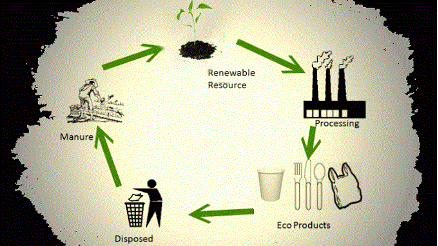
Bioplastics can form a closed-loop lifecycle.
Bioplastics
Bioplastics is a sweeping expression for many “biobased polymers”. Some are greener than The Jolly Green Giant’s pants and others are as suspect as VW’s Diesel engine programme.
They are typically made from renewable biomass such as vegetable fats, sugar cane, corn starch, sawdust and food waste.
You know those packing peanuts that look like Wotsits and smell like Sugar Pu s? Bioplastic.
Another prime example of big companies harnessing plant based plastic is Coca-Cola and its “PlantBottle”.
The new, sustainable, way to buy promotional merchandise.
ConsThe raw material for bioplastic requires a lot of farmland to grow. They also use a lot of water to
produce.
Whilst growing and during production pollution can be caused by fertilizer, pesticides and other
chemicals. Contrary to popular belief, Not all Bioplastics are biodegradable or
compostable.
Inevitably bioplastics can end up in landfill. Deprived of oxygen, it can release methane, a greenhouse gas 23 times more potent than
carbon dioxide.
Recycling bioplastic is challenging and currently not economically viable. It requires a separate recycling stream to regular plastic otherwise it stands to contaminate
the recycling process.